中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 848-853.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.06.005
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
植入含感觉神经束和血管束组织工程骨修复股骨大段骨缺损:降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体的中长期表达
陈思圆1,王 簕2,江 汕3,裴国献4
- 1广东医科大学附属医院骨科中心,广东省湛江市 524000;2广州医科大学附属第三医院骨科,广东省广州市 510150;3南方医科大学南方医院创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510515;4解放军第四军医大学西京骨科医院,陕西省西安市 710312
Implantation of tissue-engineered bone with vascular bundles or sensory nerve tracts for large femoral defects: the middle- and long-term expression of calcitonin gene related peptide type I receptor
Chen Si-yuan1, Wang Le2, Jiang Shan3, Pei Guo-xian4
- 1Orthopedic Center, the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopaedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Traumatic Orthopaedics, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 4Department of Orthopaedics, Xijing Hospital of the Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an 7100312, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
植入含感觉神经束和血管束的组织工程骨修复兔股骨大段骨缺损:植入含血管束在组织工程骨中形成新生血管网,重建血液循环,为成骨活动提供营养,并可带走局部代谢产物,并可提高移植骨的抗感染和修复能力;植入的感觉神经束可在组织工程骨中通过出芽形式生长形成新生神经网,感觉神经可释放神经肽,作用于种子细胞,调节其成骨功能;血管束周围结缔组织带劲部分胶原纤维,参与成骨。
背景:前期实验证实,植入含血管束或感觉神经的组织工程骨促成骨程度与其内的感觉神经肽受体表达相关。
目的:观察植入含感觉神经束和血管束的组织工程骨修复兔股骨大段骨缺损,对降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体中长期表达的影响。
方法:取36只新西兰大白兔,制作单侧股骨1.5 cm缺损模型,随机分3组,感觉神经组于骨缺损处植入成骨诱导7 d的骨髓间充质干细胞-β-磷酸三钙组织工程骨,并在组织工程骨侧槽内植入自体感觉神经束;血管束组于骨缺损处植入成骨诱导7 d的骨髓间充质干细胞-β-磷酸三钙组织工程骨,并在组织工程骨侧槽内植入自体股血管束;空白对照组于骨缺损处植入成骨诱导7 d的骨髓间充质干细胞-β-磷酸三钙组织工程骨。植入后24,48周,进行X射线、免疫组织学及荧光定量PCR检测。
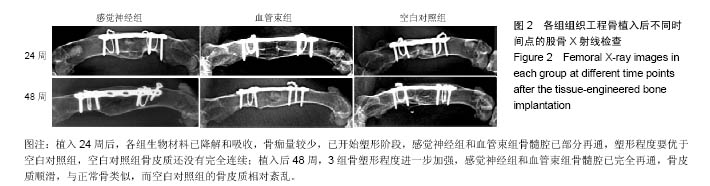
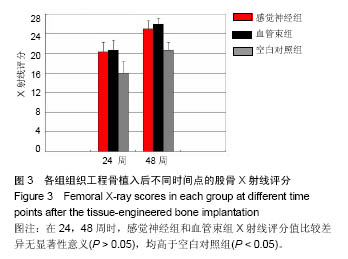
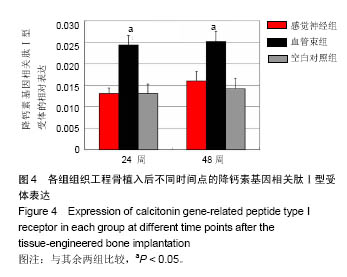
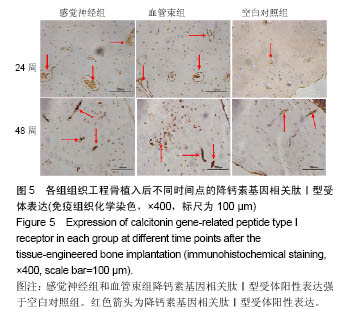
结果与结论:①X射线检查:感觉神经组、血管束组X射线评分高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),感觉神经组、血管束组X射线评分比较差异无显著性意义;②荧光定量PCR检测:血管束组降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体表达量高于感觉神经组、空白对照组(P < 0.05),感觉神经组与空白对照组比较差异无显著性意义;③免疫组织化学观察:感觉神经组、血管束组降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体阳性表达强于空白对照组;④结果表明:植入含血管束的组织工程骨可促进降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体的表达。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)